|
CycloBranch
|
|
CycloBranch
|
The settings dialog is opened using the command "Search -> Settings... ". Use F1 to open this help.
This page describes only a selection of parameters important for 'De Novo Search Engine - MS/MS' mode. For other parameters, see the page for dereplication mode.
See also the Tutorials 1-5 (CycloBranch 1.x).
Select the type of peptide or polyketide.
The type 'Other' can be used for fragmentation metabolites. See more details here
Number of a spectrum to be processed in a LC-MS/MS data file. The number may be different from an internal scan number stored in the input data file.
Enter the precursor mass-to-charge (m/z) ratio. The value is decharged automatically. The precursor m/z ratio in the input peaklist file is ignored.
Enter the formula of a precursor ion adduct (e.g., Na, K, Li). H is used by default if the field is empty. m/z ratios of theoretical peaks are shifted by mass of adduct. If a metal is used (e.g., FeH-2) and the option "Generate Full Isotope Patterns" is disabled, the peaks of isotopes having natural abundances greater than 3% are generated automatically in theoretical peaklists next to the peaks of most abundant isotopes.
Examples of precursor ion adducts:
| Precursor Ion | Precursor Adduct |
|---|---|
| [M+H]+ | H or empty |
| [M+Na]+ | Na |
| [M+K]+ | K |
| [M-H]- | H or empty |
| [M+Fe-2H]+ | FeH-2 |
| [M+Fe-3H+Na]+ | FeH-3Na |
| [M+Fe-4H]- | FeH-4 |
| [M+Al-2H]+ | AlH-2 |
| [M+Si-3H]+ | SiH-3 |
| [M+Zn-H]+ | ZnH-1 |
| [M+Zn-2H+Na]+ | ZnH-2Na |
| [M+Zn-3H]- | ZnH-3 |
Enter the charge of precursor ion. Negative values are allowed. The charge of precursor ion in the input peaklist file is ignored.
Enter the precursor m/z error tolerance in ppm. The value in the input peaklist file is ignored.
Enter the fragment m/z error tolerance [ppm].
A text file containing a database of building blocks. See Format of Building Blocks Databases.
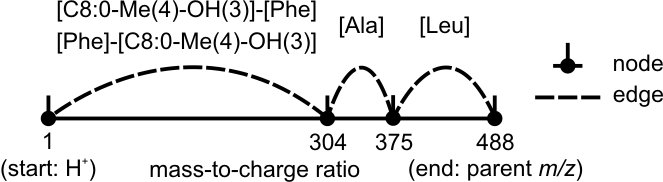
Maximum number of combined building blocks to skip a gap in a de novo graph. A small value speeds up the search and vice versa. Depending on the position of a gap between peaks in a spectrum, the three different values are set up:
In the following scheme, beauverolide I is detected. Since the peak between m/z 1 and 304 is missing, the minimum values start/middle/end are 2/1/1. Otherwise, beauverolide I is not detected when "Incomplete Paths in De Novo Graph" is set up to "keep" or "remove".
Tip: When an unknown molecule is analyzed, check peptide sequence tags first. Use the following settings:
When a branched peptide is analyzed, the minimum values are 1/2/1 (the branch is in the middle), 1/1/3 (the branch is at the end) or 3/1/1 (the branch is at the beginning). If smaller values are used, the branch cannot be detected. See also Branched Sequence Detection.
When a branch-cyclic peptide is analyzed, the minimum values are 1/2/1, 1/1/2 or 2/1/1. See also Branch-cyclic Sequence Detection.
The operation to be performed with edges forming incomplete paths (i.e., the paths which do not lead from the start node or do not lead to the end node). The following options can be selected:
Enter the maximum cumulative mass of combined blocks (0 = the maximum mass is unlimited). A small value speeds up the search and vice versa.
A text file containing a list of N-terminal and C-terminal modifications. See Format of Modification Databases.
Disable the filtering of compounds by precursor mass.
Generate internal fragment ions in theoretical spectra. This feature is currently available only for branch-cyclic peptides.
Generate scrambled fragment ions of cyclic peptides in theoretical spectra.
The water molecule is subtracted from all theoretical N-terminal fragment ions and the theoretical precursor mass. This feature is useful if a linear peptide includes a small cycle close to the N-terminus. If the linear polyketide is selected as the peptide type, the water molecule is subtracted only from the precursor ion.
The water molecule is subtracted from all theoretical C-terminal fragment ions and the theoretical precursor mass. This feature is useful if a linear peptide includes a small cycle close to the C-terminus. If the linear polyketide is selected as the peptide type, the water molecule is subtracted only from the precursor ion.
Keep only polyketide sequence candidates whose ketide building blocks are in the regular order [water eliminating block]-[2H eliminating block]-[water eliminating block]-[2H eliminating block], etc.
A score for peptide-spectrum matches. The following scores are predefined:
A maximum length of an output report with peptide sequence candidates.
Each peptide sequence candidate generated from a de novo graph must fulfil the peptide sequence tag. Otherwise, its theoretical spectrum is not generated and the peptide sequence candidate is excluded from the search. A name of a building block must be enclosed in '[' and ']'. Enclosed building blocks must be separated by '-'. A branch of a branched or a branch-cyclic peptide must be enclosed in "\(" and "\)". Additional backslashes must be used because of a special meaning of '(' and ')' in regular expressions. The tag can be a regular expression in ECMAScript syntax except symbols '[' and ']' which have a special meaning and enclose a building block. Examples of peptide sequence tags:
[Val]-[Lac]-[Val]-[Hiv] (a peptide sequence candidate must contain the following subsequence: valine, lactic acid, valine, 2-hydroxyisovaleric acid) ([Val]-[Lac]-[Val]-[Hiv]-*){3} (the tag must be repeated exactly 3x in a peptide sequence candidate, i.e., the tag corresponds to valinomycin; the symbol '*' means that the previous symbol '-' may or may not be present) [Pro]-[Ile]-[Ile]\([Orn]-[N-Ac-Ile]\)[Phe] (a tag corresponding to the branched peptide linearized pseudacyclin A) Note that a peptide sequence candidate is kept if the tag is detected in any linearized sequence of a cyclic, branched or branch-cyclic peptide sequence. See also Format of Sequence Databases.
The following types of fragment ions are defined for MS/MS spectra:
Note that y-ions are not supported when cyclic peptides are searched. Fragment ions series of linear and cyclic polyketides are described on extra pages. See Nomenclature of Linear Polyketide Series and Nomenclature of Cyclic Polyketide Series.
Buttons:
Define and select the types of neutral losses or chemical elements which will be used when generating theoretical spectra.
Buttons:
The default neutral losses are defined as follows:
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| H2O | water |
| NH3 | ammonia |
| CO | formyl group |
| CO2 | carboxyl group |
| CONH | carbamyl group |
| CH2 | shortened carbon chain |
| C6H4 | benzene ring removal |
| CH2N2 | part of Arg side chain |
| CH2O | Ser side chain |
| CH2S | Cys side chain |
| C4H9N | Lys side chain |
| C4H4N2 | His side chain |
| C4H9N3 | Arg side chain |
| C9H7N | Trp side chain |
The molecular formulas of proteinogenic amino acids side chains can be optionally combined from the default values as follows:
| Amino acid | Side chain | Amino acid | Side chain | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gly | - | Asp | C2H2O2 (CH2+CO2) | |
| Ala | CH2 | Gln | C3H5NO (CH2+CH2+CONH) | |
| Ser | CH2O | Lys | C4H9N | |
| Pro | C3H4 (not defined) | Glu | C3H4O2 (CH2+CH2+CO2) | |
| Val | C3H6 (CH2+CH2+CH2) | Met | C3H6S (CH2+CH2+CH2S) | |
| Thr | C2H4O (CH2+CH2O) | His | C4H4N2 | |
| Cys | CH2S | Phe | C7H6 (CH2+C6H4) | |
| Leu | C4H8 (CH2+CH2+CH2+CH2) | Arg | C4H9N3 | |
| Ile | C4H8 (CH2+CH2+CH2+CH2) | Tyr | C7H6O (CH2O+C6H4) | |
| Asn | C2H3NO (CH2+CONH) | Trp | C9H7N |
In some cases, the list of neutral losses can be replaced by a list of chemical elements (e.g. H, C, O, N, S, and P). This is useful if an experimental spectrum contains peaks corresponding to ions with unknown neutral losses, if a metabolite (i.e. a non-peptidic compound) is fragmented or if the mode 'Compound Search - MS, LC-MS, MSI' is used.
Maximum number of combined neutral losses.
A peptide sequence which you are searching for or a peptide sequence tag. A peptide sequence must be entered if "Mode" is set up to "Compare Peaklist(s) with Spectrum of Searched Sequence". Otherwise, the option is similar to "Peptide Sequence Tag" with a difference that a peptide sequence candidate is not removed from the search but it is just highlighted in the output list of peptide sequence candidates. If "Compare Peaklist(s) with Spectrum of Searched Sequence" mode is used, the only possible format of the expression is a peptide sequence (e.g.,
[Val]-[Lac]-[Val]-[Hiv]-[Val]-[Lac]-[Val]-[Hiv]-[Val]-[Lac]-[Val]-[Hiv]
or
[Pro]-[Ile]-[Ile]\([Orn]-[N-Ac-Ile]\)[Phe]
). Regular expressions like
([Val]-[Lac]-[Val]-[Hiv]-*){3}
are not supported in this mode. See also Format of Sequence Databases.
Button 'Edit (CTRL + E)' - Edit the peptide sequence using the Draw Peptide Tool. The sequence is imported into the draw peptide tool and visualized if its syntax is correct (see also Format of Sequence Databases).
A name of an N-terminal modification which belongs to the searched peptide. The name must be defined in N-/C-terminal Modifications File.
A name of a C-terminal modification which belongs to the searched peptide. The name must be defined in N-/C-terminal Modifications File.
A name of an N-terminal or C-terminal modification which belongs to a branch of a searched peptide (branched and branch-cyclic peptides only). The name must be defined in N-/C-terminal Modifications File.